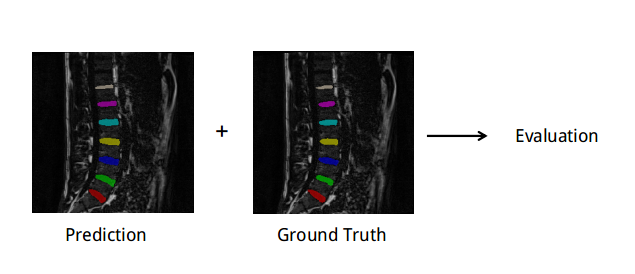
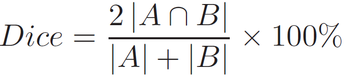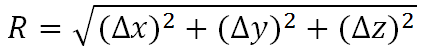Evaluation Metrics1.Rules for evaluation(1) Multi Label PredictionIf the prediction is not binary, we directly do the evaluation.
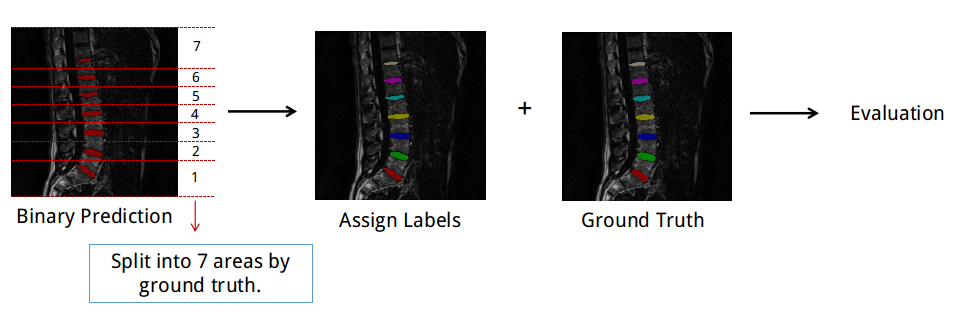
(2) Binary Label PredictionIf the prediction is binary, we first assign labels to each intervertebral disc based on ground truth segmentation and then do the evaluation. As shown in the figure below, the complete image space is spitted into 7 sections, corresponding to 7 intervertebral discs in the ground truth segmentation.
The performance of each submitted method will be evaluated based on both localization and segmentation results.
2. Three Metrics for evaluationFor each test image, the evaluation result would be the average value of 7 intervertebral discs. And for each metric, the final evaluation result would be the average value of all test cases.
|
(1) Dice Overlap CoefficientsThe Dice metric measures the percentage of correctly segmented voxels. Dice is computed by
where A is the sets of foreground voxels in the ground-truth data and B is the corresponding sets of foreground voxels in the segmentation result, respectively. Larger Dice metric means better segmentation accuracy.
(2) Average Absolute DistanceAverage Absolute Distance (ASD) is a metric measures the average absolute distance from the ground truth disc surface and the segmented surface. Smaller average absolute distance means better segmentation accuracy.
For each intervertebral disc, the ASD will be set as maximum value (458.24mm) if the Dice value is less than 0.1% and additionally the number of segmented voxels assigned to this disc is smaller than 5% of the total voxels of the ground truth segmentation. In such a case, a method is regarded missing the segmentation of the disc completely.
(3) Localization distanceThe equation of localization distance R is computed by
where ∆x is the absolute difference between X axis of the identified IVD center and the ground truth IVD center calcaulated from the ground truth segmentation, ∆y is the absolute difference between Y axis of the identified IVD center and the ground truth IVD center, and ∆Z is the absolute difference between Z axis of the identified IVD center and the ground truth IVD center. Smaller localization distance means better segmentation accuracy.
For each intervertebral disc, the Localisation distance will be set as maximum value (458.24mm) if the Dice value is less than 0.1% and additionally the number of segmented voxels assigned to this disc is smaller than 5% of the total voxels of the ground truth segmentation. In such a case, a method is regarded missing the segmentation of the disc completely.
|